Thorough Insights into Concrete Scanning Procedures
Thorough Insights into Concrete Scanning Procedures
Blog Article
Past the Surface: Leveraging Advanced Concrete Scanning Techniques for Unmatched Accuracy and Understanding
Advanced concrete scanning strategies have emerged as essential tools in this search, offering a look under the surface to reveal a globe of vital insights. By harnessing advanced technologies, experts can reveal anomalies, examine the problem of concrete structures, and make informed decisions that form the program of tasks.
Importance of Advanced Concrete Scanning
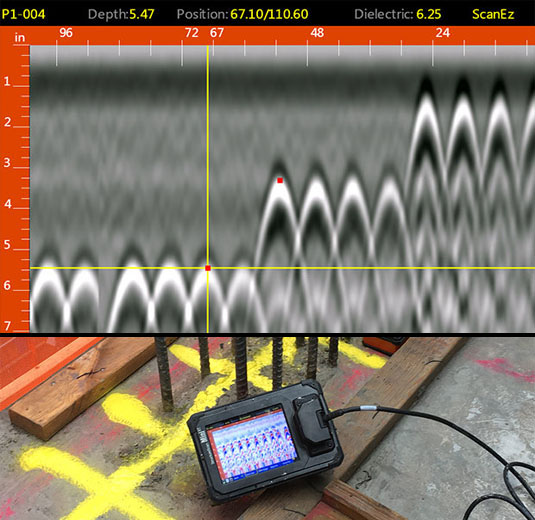
The importance of using sophisticated concrete scanning strategies hinges on the exceptional accuracy they offer for discovering sub-surface abnormalities and making certain architectural integrity. By utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR), electromagnetic induction, and advanced sonar imaging, building and construction specialists can dive under the surface area of concrete frameworks with a degree of precision that much exceeds standard inspection techniques. Concrete Scanning. These methods allow the recognition of concealed threats like rebar deterioration, spaces, avenues, or post-tension wires that can endanger the stability and security of a structure gradually
Additionally, advanced concrete scanning offers indispensable insights into the total condition of a concrete element without the demand for intrusive procedures, reducing the risk of creating damage throughout the assessment procedure. The capacity to identify the exact area and deepness of potential concerns permits targeted repair work and upkeep, eventually prolonging the life expectancy of the framework and optimizing its efficiency. Basically, the importance of innovative concrete scanning can not be overstated in the world of building and construction and infrastructure upkeep, where precision and integrity are vital.
Types of Cutting-Edge Technologies
Abnormalities and Flaw Detection

In enhancement to GPR, concrete scanning strategies like thermography and impact-echo screening are likewise effective in discovering issues and abnormalities. By leveraging these sophisticated techniques, specialists can proactively resolve structural concerns, making certain the durability and security of concrete frameworks.
Assessing Concrete Problem
How can engineers properly assess the problem of concrete structures to ensure their long life and safety? Different innovative concrete scanning methods are used for this purpose. Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is frequently made use of to examine the inner structure of concrete, identifying spaces, fractures, and various other anomalies that may endanger its strength.
Moreover, aesthetic examination stays a fundamental part of concrete condition analysis. Engineers aesthetically check out the surface for signs of degeneration, such as spalling, fracturing, or staining. Integrating non-destructive screening approaches with aesthetic examinations permits a comprehensive assessment of concrete condition, allowing designers to recognize possible concerns beforehand and implement timely maintenance click or repairs. By leveraging these advanced methods, engineers can guarantee the long-lasting toughness and security of concrete structures.
Enhancing Decision-Making Procedures
In the realm of infrastructure management, maximizing decision-making procedures is critical for ensuring the effective upkeep and durability of concrete frameworks. Improved decision-making processes in concrete management entail using advanced scanning strategies to collect thorough data on the problem of structures. By leveraging modern technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and 3D imaging, stakeholders can make enlightened decisions regarding replacement, reinforcement, or repair service techniques.
These progressed scanning techniques supply indispensable understandings into the inner composition of concrete, identifying possible issues such as voids, splits, or corrosion that might not be visible on the surface area. This level of in-depth details allows for positive upkeep preparation, reducing the threat of structural failures and boosting the total lifespan of concrete structures.
In addition, by integrating electronic documentation and analysis tools right into the decision-making procedure, stakeholders can track the evolution of concrete problems over time, enabling predictive maintenance techniques and enhancing resource allotment. Eventually, the combination of sophisticated concrete scanning methods improves decision-making procedures by providing unmatched precision, understanding, and performance in framework monitoring.
Final Thought
To conclude, progressed concrete scanning techniques use unequaled accuracy and insight in discovering anomalies, defects, and assessing the condition of concrete frameworks. By leveraging sophisticated technologies, decision-making procedures can be improved, resulting in more efficient and informed solutions for keeping official source and fixing concrete infrastructure. These techniques play an essential duty in making certain the security and longevity of concrete frameworks, making them a crucial tool in the field of building and engineering.
In addition, advanced concrete scanning gives important understandings into the total problem of a concrete element without the demand for invasive actions, lessening the risk of creating damage during the assessment procedure - Concrete Scanning. Another cutting-edge technology is 3D X-ray scanning, which supplies in-depth photos of the internal framework of concrete, offering useful details without the need for harmful link testing. Furthermore, Concrete Cover Meters are used to gauge the density of concrete cover over reinforcement bars properly. Enhanced decision-making processes in concrete administration entail utilizing innovative scanning techniques to collect comprehensive data on the problem of frameworks.In conclusion, advanced concrete scanning strategies supply unequaled precision and insight in discovering abnormalities, issues, and assessing the condition of concrete frameworks
Report this page